-
ꁸ Top
-
ꂅ +86 159 1059 4147
-
ꀥ WhatsApp



-
HOME
-
ABOUT
-
PRODUCTS
- DRILLING TOOLS
- DRILLING MOTORS
- STABILIZERS
- DRILL COLLARS
- DRILLING JARS
- HYDRAULIC AGITATOR
- ANTI STICK-SLIP TOOL
- MULTIPLE ACTIVATION BYPASS VALVE
- DRILL PIPES
- NON-ROTATING PROTECTOR
- X-OVER & SUBS
- DRILL BITS
- MICRO REAMER
- FISHING TOOLS
- RELEASING SPEAR
- RELEASING AND CIRCULATING OVERSHOT
- REVERSE CIRCULATION JUNK BASKET
- JUNK SUB
- FISHING MAGNET
- SAFETY JOINT
- TAPER TAP
- DIE COLLAR
- IMPRESSION BLOCK
- DITCH MAGNET
- MILLING SHOES
- WASHOVER PIPE
- IBOPs
- KELLY VALVE
- FLOAT VALVE
- FULL OPENING SAFETY VALVE
- TOP DRIVE IBOP
- INSIDE BOP
- DROP-IN CHECK VALVE
- WELLBORE CLEANING TOOLS
- CASING SCRAPER
- NON-ROTARY CASING SCRAPER
- CASING BRUSH
- CUTTING BED IMPELLER
- STRING MAGNET
- ROTARY CASING GUIDER
- CASING CUTTER
- SECTION MILL
- WELLHEAD TOOLS
- ELEVATORS
- ELEVATOR LINKS
- POWER TONGS
- MANUAL TONGS
- SLIPS
- SPIDERS
- SPINNING WRENCH
- BUSHINGS
- DRILLING EQUIPMENTS
- MUD PUMP
- VALVE SEAT AND BODY
- PISTON
- CYLINDER LINER
- HYDRAULIC BUCKING UNIT
- JAR TESTER
- FRAC PUMP VALVE RUBBER
- FRAC PUMP VALVE BODY
- FRAC PUMP VALVE SEAT
- FRAC PUMP PLUNGER PACKING
-
PRESS
-
CONTACT


-
HOME
-
ABOUT
-
PRODUCTS
- DRILLING TOOLS
- DRILLING MOTORS
- STABILIZERS
- DRILL COLLARS
- DRILLING JARS
- HYDRAULIC AGITATOR
- ANTI STICK-SLIP TOOL
- MULTIPLE ACTIVATION BYPASS VALVE
- DRILL PIPES
- NON-ROTATING PROTECTOR
- X-OVER & SUBS
- DRILL BITS
- MICRO REAMER
- FISHING TOOLS
- RELEASING SPEAR
- RELEASING AND CIRCULATING OVERSHOT
- REVERSE CIRCULATION JUNK BASKET
- JUNK SUB
- FISHING MAGNET
- SAFETY JOINT
- TAPER TAP
- DIE COLLAR
- IMPRESSION BLOCK
- DITCH MAGNET
- MILLING SHOES
- WASHOVER PIPE
- IBOPs
- KELLY VALVE
- FLOAT VALVE
- FULL OPENING SAFETY VALVE
- TOP DRIVE IBOP
- INSIDE BOP
- DROP-IN CHECK VALVE
- WELLBORE CLEANING TOOLS
- CASING SCRAPER
- NON-ROTARY CASING SCRAPER
- CASING BRUSH
- CUTTING BED IMPELLER
- STRING MAGNET
- ROTARY CASING GUIDER
- CASING CUTTER
- SECTION MILL
- WELLHEAD TOOLS
- ELEVATORS
- ELEVATOR LINKS
- POWER TONGS
- MANUAL TONGS
- SLIPS
- SPIDERS
- SPINNING WRENCH
- BUSHINGS
- DRILLING EQUIPMENTS
- MUD PUMP
- VALVE SEAT AND BODY
- PISTON
- CYLINDER LINER
- HYDRAULIC BUCKING UNIT
- JAR TESTER
- FRAC PUMP VALVE RUBBER
- FRAC PUMP VALVE BODY
- FRAC PUMP VALVE SEAT
- FRAC PUMP PLUNGER PACKING
-
PRESS
-
CONTACT
What is the Different Types and Functions of Drilling Stabilizer?
Drilling stabilizer is generally connected to a section of drill pipe string or drill bit close to large-diameter drilling tools and used to stabilize the drilling direction. We will discuss about the different types and functions of drilling stabilizers used in drilling operation in this article.
Types of drilling stabilizers
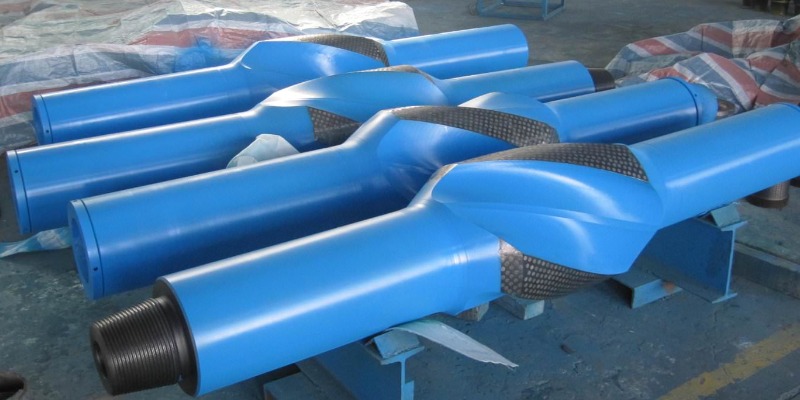
1. Integral Blade Stabilizers
Integral blade stabilizers are widely used in drilling operations due to their exceptional strength and durability. These stabilizers feature a one-piece construction, making them highly stable under the most demanding drilling conditions. The blades are seamlessly forged with the body, ensuring maximum strength and resistance against wear and tear. Integrated blade stabilizers can be divided into two categories according to their installation positions:


-
Near bit stabilizer (also called downhole stabilizer): only used at the bit, with box connections both ends;
-
String stabilizer: longer than the near bit stabilizer, and has pin connection at the lower end and box connection at the upper end;
2. Sleeve Stabilizers
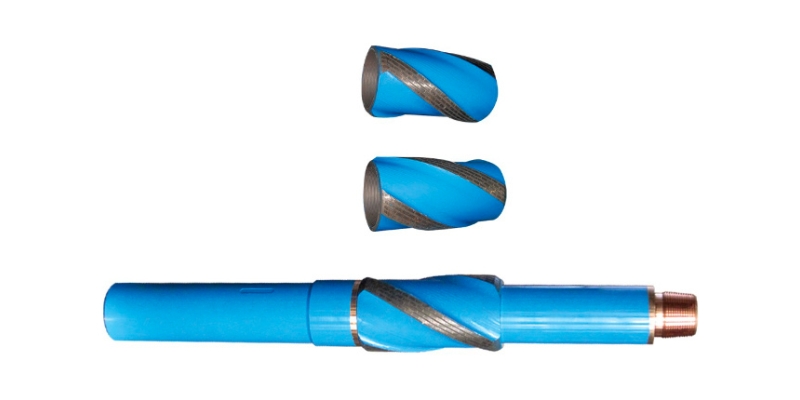
Sleeve stabilizers, also referred to as variable gauge stabilizers, offer versatility in hole sizes. These stabilizers consist of an outer sleeve that can be adjusted to accommodate different wellbore dimensions. The adjustable sleeve allows operators to optimize stability in various formations, improving drilling efficiency. Sleeve stabilizers are particularly advantageous in applications where drilling through different geological formations is required.
3. Replaceable Blade Stabilizers
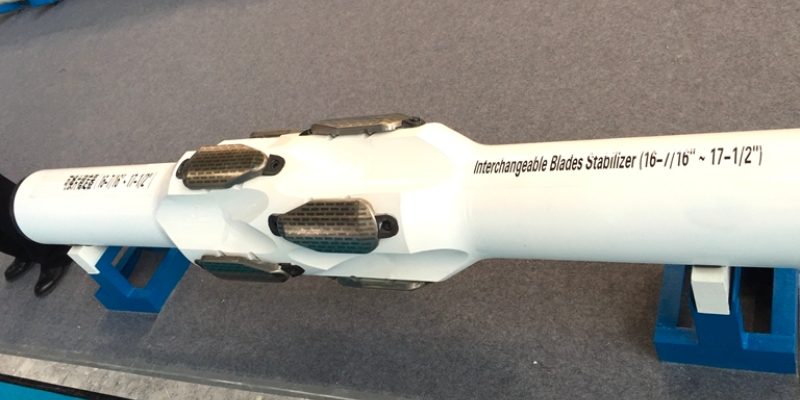

Replaceable (or interchangeable) blade stabilizers provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness. These stabilizers feature a modular design, allowing the blades to be easily replaced when worn out or damaged, without the need to replace the entire stabilizer. By utilizing replaceable blades, operators can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs while ensuring consistent drilling performance. This type of stabilizer is particularly suitable for extended drilling projects.
4. Non-Rotating Stabilizers
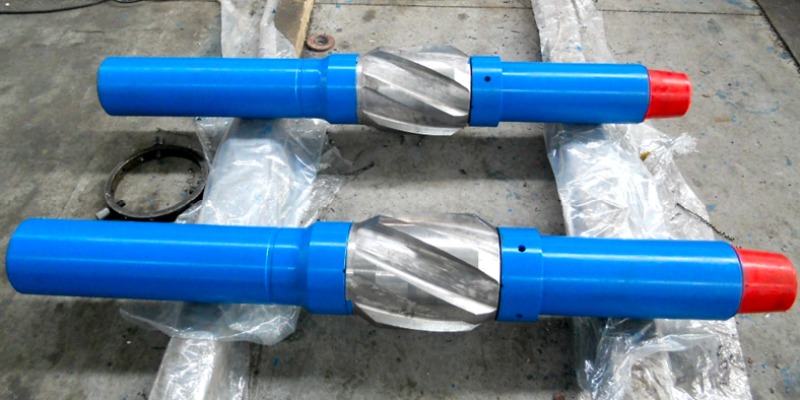

Non-rotating stabilizers, also known as fixed blade stabilizers, are specifically designed to minimize drillstring rotation. These stabilizers feature a locked blade configuration that prevents any rotational movement, resulting in reduced torque and vibrations. Non-rotating stabilizers help maintain wellbore trajectory, prevent differential sticking, and improve the overall drilling process. They are commonly employed in sensitive formations and directional drilling operations.
5. Roller Reamer
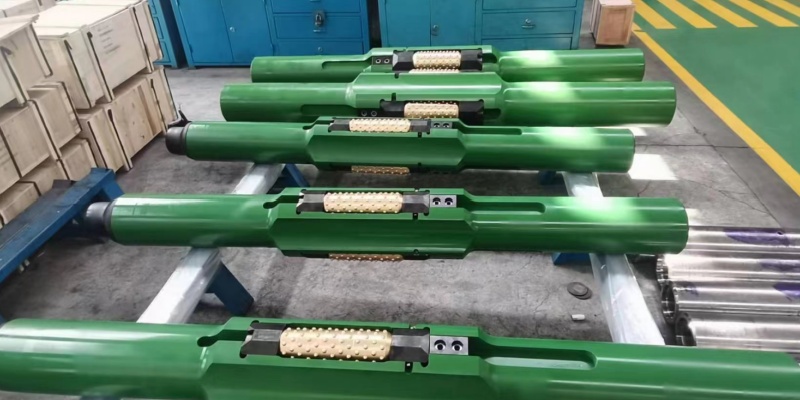

Roller reamer provides stabilization action by centralizing the BHA, minimizing down-hole vibrations, preventing the BHA from resting on the low side of the deviated hole, and minimizing BHA fatigue. All parts of the tools are made of special alloy steel and heat treated for hardness. As formations or drilling requirements change, cutters can easily be replaced any part at rig site without the use of welding, cutting or special tools.
Functions:
-
Controlling the wellbore trajectory: The stabilizer mainly plays a guiding and centering role in the bottom hole assembly (BHA). It is installed at a position that controls the well inclination angle and wellbore curvature within the specified range, and also concentrates most of the weight of the drill collar on the drill bit, reduce the non-wellbore center force and other external forces borne by the drill string and the drill bit. With the development of stabilizers and the large-scale mining of horizontal wells and directional wells, stabilizers have become an indispensable bottom hole tool in modern well trajectory control technology.
-
Hole expansion: In curved wellbore or wellbore diameter reduction, it drills together with the drill string, and the chamfer at the transition between its lower end body and the working section plays a certain hole expansion role.
-
Conditioning of the well wall: During the process of frictional contact between the stabilizer and the well wall, the well wall is trimmed to varying degrees, making the well wall smoother and smoother, and improving the quality of the well body.
Drilling stabilizers are indispensable tools in the oil and gas industry, ensuring drilling stability, minimizing vibrations, and optimizing drilling performance. Whether it’s maintaining hole-gauge control, accommodating various wellbore sizes, or preventing drillstring rotation, there is a drilling stabilizer designed to meet the demanding requirements of every drilling operation.
FAQs
1. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a drilling stabilizer?
When choosing a drilling stabilizer, factors such as formation characteristics, well trajectory, required hole size, and drilling objectives should be considered. It is crucial to select a stabilizer that can effectively address the specific challenges and requirements of the drilling operation.
2. How can drilling stabilizers help improve drilling efficiency?
Drilling stabilizers aid in minimizing wellbore deviation, reducing vibrations, and controlling hole-gauge, which ultimately leads to smoother drilling operations, increased ROP (Rate of Penetration), and enhanced overall drilling efficiency.
3. What maintenance practices should be followed for drilling stabilizers?
Regular inspection, cleaning, and proper storage are essential for maintaining drilling stabilizers. Replaceable blade stabilizers require monitoring and timely replacement of worn-out blades. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines ensures optimal performance and prolongs the stabilizer’s lifespan.
Tags: Drilling Stabilizers
Drilling stabilizer, sometimes called balancer, is a tool that stabilizes downhole drilling tools and prevents deviation in oil, natural gas and geological exploration drilling projects.
2023-09-26





